Mitad del Mundo

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Mitad del Mundo is a touristic attraction built in 1979 by order of Patricio Romero barberia with the intent of promoting Ecuador’s identity and the European 18th-century geodesic missions. The main entrance is a large corridor with some sculptures with the most important men who took measures in the first geodesic mission like La Condamine or…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
PEDRO VICENTE MALDONADO (Riobambam 1704 – London, 1748)
- Thanks to his ample knowledge of geodesy and geography, he was one of the key members of the First Geodesic Mision.
- He was the first latin american to join the Paris Academy of Sciences.
- He drew the first geographical map of the Royal Audiencia of Quito.
- He is attributed with building the commercial route between Quito and Esmeraldas.
- Due to his notable work, he was dubbed “Knight of the Royal Chamber” by King Philip V of Spain in 1746.
- His remains lie in St. James’s Church of England.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
ANTONIO DE ULLOA (Sevilla, 1716 – Isla de León, 1795)
- He was one of the sailors sent by King Philip V of Spain to form part of the Geodesic Mission.
- He went to Paris with La Condamine where he became a member of the Academy of Sciences.
- Due to his scientific work, he published “Noticias de America” (News of the Americas) in 1772.
- Together with Jorge Juan y Santacilia, he wrote the famous report entitled “Noticias Secretas” (Secret News) to the King of Spain about the state of his colonies.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
JORGE JUAN Y SANTA CILIA (Alicante, 1713 – Madrid, 1773)
- He was a Spanish scientist, mathematician, naval officer and mariner. He was appointed member of the French Geodesic Mission by the King of Spain, Philip V.
- He remained in South America for many years with the purpose of studying the political and social situations in the Spanish territories.
- He wrote “Relación Histórica del Viaje a la América Meridional” (History of the Journey to Meridional America) with Antonio de Ulloa. It was published in Madrid in 1748.
The expedition was former by the French scientists La Condamine, Godin, Jussieu, Bouguer, Morinville, Verguin, Godin des Odonnais, Seniergues and Hugot, and the Spaniards Jorge Juan and Antonio de Ulloa. They left La Rochelle on May 16th, 1735 and arrived at Manta on March 9th, 1736. La Condamine separated himself from the others and performed the first measurements and observations on the coast of Manabi and on June, the members of the mission met again to select the most adequate place for a base that would be used for the necessary triangulation.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
On the top of the main monument there is a big world with a rounding equatorial line…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
… and inside you can see that the rotation of the water is determined by other factors like the initial rotational direction (Coriolis effect!):

Photography by Carlos Dorce
CORIOLIS
It is the effect
It is the effect observed in a rotating reference system when an object is moving respect to that system. Its influence can be detected in the rotation of hurricanes, ocean currents and trade winds.
The place is lovely and the views from the top of the monument are wonderful!

Photography by Carlos Dorce
There also are some sundials like these ones:

Photography by Carlos Dorce

Photography by Carlos Dorce
In the different museums, it is possible to learn more things about the geodesic mission and the instruments of measurement used by the scientists:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Of course, if you go to Mitad del Mundo you must play with your feet and the equatorial line: one foot in the North and one foot in the South!

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Location: Mitad del Mundo (map)
George Boole’s 200th Birthday
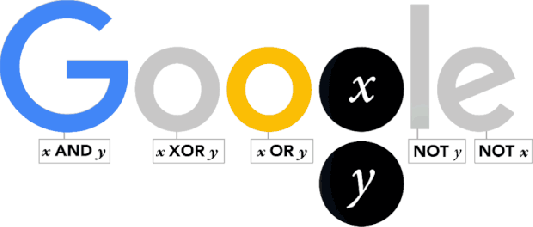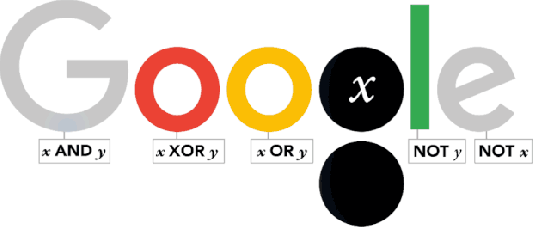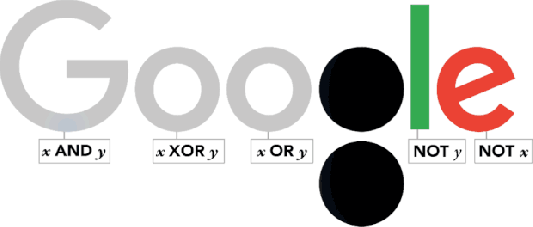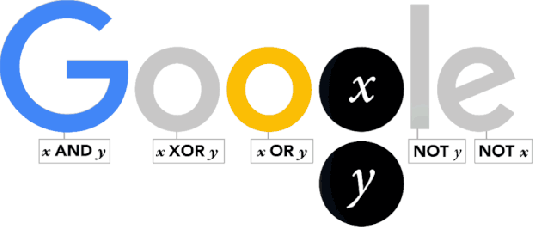
George Boole was born in Lincoln (Lincolshire) on November 2, 1815. Thus, today is a great day in history of Mathematics and Google has dedicated this interesting doodle to him.
This is the information about this special doodle:
Here’s an easy, yes-or-no question:
Is the universe complex?
YES, of course, you could say; it would be crazy to think otherwise! But on the other hand, British mathematician George Boole taught us that NO, things can be seen as relatively simple; any values can be pared down to yes or no, true or false, or 0 or 1 (which, here at Google, is our personal favorite).
In 1849, Boole was appointed as the first Professor of Mathematics at University College Cork, where he pioneered developments in logic and mathematics. His beautiful binary “Boolean” system was detailed in An Investigation of the Laws of Thought in 1854, which inevitably enabled revolutionary thinking in not just logic and math, but also engineering and computer science.
As one of the most important scientists to have ever worked in Ireland, Boole effectively laid the foundations of the entire Information Age while working from UCC. So it’s fair to say that without George Boole, there’d be no Google! So, as a tribute to Boole’s contributions, artist Leon Hong created today’s doodle, which cycles through all the ANDs, ORs, NOTs, and even XORs of the Boolean states for two discrete variables.
A very happy 11001000th birthday to genius George Boole!
Monument to Einstein in Ulm

Photography by Carlos Dorce
This monument is located in the former Bahnhofstrasse B 135 (in 1880 renamed to Bahnhofstrasse 20) in Ulm where was placed the house where Albert Einstein was born in 1879.
The house was erected in 1871 and was destroyed in December 1944 in the bombardments of Ulm.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, and he lived in this house until the summer of 1880 when his fateher Hermann decided to move to Munich (on June 21, 1880, Hermann registered his family with Munich’s police).
This is a photography of Einstein’s birthplace before its destruction:

Location: monument to Einstein in Ulm (map)
Ptolemy and Pythagoras in Ulm

Photography by Carlos Dorce
The cathedral is one of the main attractions of Ulm because its tower is the tallest in the World (more than 161 metres!). However, one of the most interesting work of art which can be admired inside the church is the 15th century choir stalls crafted by Jörg Syrlin the Elder. There are 89 seats arranged in two rows with 90 busts of saints, Old Testament figures and classical philosophers and scholars as Ptolemy…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
…and Pythagoras:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
We must remember that Ptolemy represent the Astronomy in the Liberal Arts and Pythagoras usually represents the Arithmetic although his bust here is related with the Music.
Most of the people who visit the cathedral don’t know that this is one of the most wonderful medieval work of art which can be seen in Germany although this beautiful picture woul remain in their minds in a lot of years.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Location: Cathedral of Ulm (map)
Kepler’s last home in Regensburg

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Kepler’s last home is this orange house located in Keplerstrasse 5 in Regensburg. Reading the famous Kepler’s biography written by Max Caspar:
[…] On November 2 [1630] he rode, tired, on a skinny nag, over The Stone Bridge into Regensburg. He took up quarters in Hillebrand Billj’s house in the street now named after him. This acquaintance was a tradesman and later an innkeeper.
Only a few days after his arrival Kepler came down with an acute illness. His body was weakened by much night study, by constant worry, and also by the long journey at a bad time of year. In the beginning he attributed no significance to his being taken ill. He had often before suffered from attacks of fever. He believed that his fever originated from “sacer ignis”, fire-pustules. As the illness became worse, an attempt was made to help him by bleeding. But soon he began to lose consciousness and became delirious. Several pastors visited him and “refreshed him with the vitalizing water of consolation”. It is not said anywhere that holy communion was afforded him. In the throes of death Pastor Christoph Sigmund Donauer rendered him aid. When, almost in the last moment of his life, he was asked on what he pinned his hope of salvation, he answered full of confidence: only and alone on the services of Jesus Christ; in Him is based, as he wanted to testify firmly and resolutely, all refuge, all his solace and welfare. At noon on November 15 this pious man breathed his last. […].
A plaque on the facade says that this is the house which I was looking for when I have arrived at Regensburg:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Bad luck! This small museum is only open in the weekends and it’s possible to rent a guided visit only for groups! I’ve not arrived here to give up! Finally, I’ve been able to visit it and the first thing that I’ve seen… the magnificent bust of the last owner of the house…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
… over a plaque in German language where it’s possible to read a little part of this story:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
The museum located in the house is very small and explains Kepler’s life and works focussing the interest in his astronomical discoveries and his three laws.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
There is also a representation of the barrels whose volume was calculated precisely by Kepler in 1615:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Another bust representing the great mathematician is in the room of the first floor next to some information about his commemorative monument also in Regensburg.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
There are a lot of Kepler’s works (which seem to be original) and this wonderful German edition of Napier’s logarithms (1631) which couldn’t be used by Kepler but exemplifies the great impact that this powerful calculator had in the beginning of the 17th century.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Of course, his Astronomia Nova, his Harmonices mundi,… and his Tabula Rudolphinae are also exhibited.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
There also are explanation about his relation with Tycho Brahe and the Copernican system and a lot of astronomical instruments like sextants, globes, compasses,…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Finally, I want to say goodbye looking at this famous portrait. This man discovered the elliptical orbits of the palnets and his obsession with numbers let him find the second and the third law. Copernicus was right and Newton will be confirm all this theories. The World was explained (Wait Einstein, wait!).

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Location: Kepler’s museum in Regensburg (map)
The mathematicians in the Walhalla

Photography by Carlos Dorce
The Walhalla is a neo-classical hall of fame which honours the most important people in German history. It was conceived in 1807 by Ludwig I of Bavaria (king from 1825 to 1848) and its construction took place between 1830 and 1842 designed by Leo von Klenze.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
The Walhalla was inaugurated on October 18, 1842 with 96 busts and 64 commemorative plaques for people with no available portrait and everything was presided by the great King Ludwig:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Among all these very famous people related with the German history there are some… of course… mathematicians who share this space with Bach, Göethe, Beethoven, Guttemberg, Luther, Otto von Bismarck,… First of all, Dürervis the great German painter from the Renaissance who applied a lot of perspective new techniques to his paintings:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
The great astronomers are also here. Regiomontanus,…

Source: Wikimedia Commons
Herschel,…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Copernicus,…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
and Kepler:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
The great Leibniz…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
and the greatest Gauss (added in 2007), also have their busts in this hall of fame:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Finally, Albert Einstein’s bust was added in 1990:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
I must say that the commemorative plaques also mention Alcuin of York, Albertus Magnus and the Venerable Bede, all ot them related with the wonderful Arithmetics!
Come to Regensburg to see this beautiful (and strange) place!
Location: Walhava in Donaustauf (map)
Another Kepler in Weil der Stadt

Photography by Carlos Dorce
This statue of Johannes Kepler is located in a garden next to Kepler’s museum in Weil der Stadt. It seems to be a private monument in a garden but it’s possible to go inside.
Location: Monument in Weil der Stadt (map)
Kepler-Museum in Weil der Stadt

Photography by Carlos Dorce
This building is the theorical Kepler’s bithplace in Weil der Stadt which hosts a very small museum about Kepler’s life and work:
At the age of six Kepler attends the German school. Continuing with Latin school he has to interrupt his attendance several times to help his parents with their work in the fields and at their inn. As a result he requires five years to complete the usual three school years.
The sickly child shows more enthusiasm at school than for hard work in the fields. His parents decide to send him to monastery school: First to the Adelberg monastery school (lower seminary) and then to Maulbronn (higher seminary).
His school comrades and teachers give him a hard time: At an early stage he starts to have his own ideas of church doctrine. His main struggle is with the meaning of Predestination and Communion.
Two celestial phenomena arouse his interest in astronomy: His mother shows him a comet, his father a lunar eclipse. Both phenomena remain in his mind for a long time. On the other hand, he never mentions his astronomy lessons in his written work.
Furthermore…
During the Age of Reformation the University of Tübingen, founded in 1477, forms the intellectual centre for Southern German Lutheran and for the Duchy of Württemberg. In 1536, Duke Ulrich orders the accomodation of poor students in Tübingen’s Stift. His aim is to ensure more graduates for loyal service in church and administration.
Coming from a humble background, Kepler wins a scholarship at the Stift. In 1589, he takes up his studies at the Faculty of Arts providing a general education, where the talented student receives many important stimuli. In particular, he studies the works of the Neoplatonists, whose ideas of a harmonically built creation make a deep impact on him.
However, his Professor of astronomy, Mästlin, influences him the most. Like a fatherly friend he familiarizes him with the ideas of Copernicus. Kepler sees an analogy in the central position of the sun to God’s omnipotence and consequently becomes a convinced advocate of the heliocentric view.
Kepler passes the baccalaureat exam at the Faculty of Arts as the second best in his class. […]. Before graduating, he accepts the position as provincial mathematician in Graz.
These were the first steps in Kepler’s life and the first thing that you see after entering the museum is the bust of this great mind:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Since 1594, as a provincial mathematician in Graz, Kepler…
[…] has to teach at the Lutheran seminary and write astrological calendars. His enthusiasm for astronomy inspires him to do his own research, and in 1596 he publishes his first work on astronomy Mysterium Cosmographicum.
He attempts to prove that a harmonic creation allows for only six planets. He regards the five regular Platonic polyhedra as elements of the planetary system, which, nested in the proper order, should determine the planet’s distance to the sun. As this approximately corresponds with the Copernican planetary distances, the work catches the attention of such important astronomers as Galileo Galieli and Tycho Brahe.
In spite of his fame, Kepler has to worry about his position in Graz. The Counter-Reformation creates great tension between the Lutheran inhabitants and the Catholic authorities. To recommend himself to the archduke Kepler dedicates a treatise to him on the solar eclipse of July 10th, 1600.
However, this does not prevent his expulsion from Graz one month later.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
So these years in Graz were the period in which Kepler dreamt of his Mysterium cosmographicum and the possibility of the God’s design for the universe based in the regular polyhedra:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
After Graz, Kepler became Tycho Brahe’s assistnat in Prague. After Tycho’s death, he assumed his position as imperial mathematician for Emperor Rudolph II:
[…] The quality of the [astronomical] data depends on the exactness of the particular orbit theory. Since all tables used around 1600 are inaccurate, Emperor Rudolph commissions Brahe and Kepler with the creation of the Tabulae Rudolphinae in 1601. When Brahe dies in the same year Kepler has to continue the work on his own.
It takes 22 years to complete the final version of the tables. Alone, the development of the elliptical orbits takes Kepler eight years. When he hears about the development of Napier’s logarithm, he integrates this into his tables and manages to simplify the calculation of orbital positions […]
Kepler discovered his first law and published it in his Astronomia nova (1609) and ten years later, he publishes his Harmonice mundi with the second and the third laws. Furthermore, Kepler had also time to wpork on infinitesimal calculus to compute the volume of some tonnels of wine:

Photography by Carlos Dorce
I could follow explaining more things about Kepler’s life and works but this museum is very small so you must visit it. And Weil der Stadt is a very beautiful town!
Location: Kepler-Museum in Weil der Stadt (map)
Johannes Kepler Monument in Weil der Stadt

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Weil der Stadt is located near Stuttgart. Johannes Kepler was born in this very veautiful town on December 27, 1571 and his memory is still there: this big statue is in the middle of the Market Square…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
… and Copernicus, Mästlin, Tycho Brahe and Jobst Bürgi are with him in this monumental sculpture.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
The four scientists are in the corners of the base of the statue and the words “Astronomia”, “Optica”, “Mathematica” and “Physica” are graved on each of the four sides.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
I must say that here we have the first (imaginary) bust of Bürgi that I know. Bürgi was one of the originators of the logarithms because Kepler said that he had seen Bürgi using logarithms in astronomical calculus (Rudolphine Tables (1627)) before their “official” first occurrence in Napier’s Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio (1614). Furthermore, Bürgi published his logarithms in his Aritmetische und Geometrische Progreß tabulen (1620) but his “red numbers” and “black numbers” couldn’t never win the “logarithms” which were the first calculator in all history.

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Notice that this statue is not very similar to this other portrait from 1620:

J.Bürgi at the age of 67. Drawing by Aegidius Sadeler (1619)
The base of the statue also have four graved images representing moments in Kepler’s life like thispicture with Kepler in the middle explaining the Copernican system…

Photography by Carlos Dorce
… with Hipparchus and Ptolemy watching how a central Sun brights in the middle of the universe.

Can you imagine Kepler investigating about his elliptical orbits?

Photography by Carlos Dorce
Next to Market Square there is his bithplace which hosts… no, no, no! Tomowwor will be another day!
Location: Weil der Stadt (map)
Abû al-Wafâ’ al-Buzjanî’s doodle
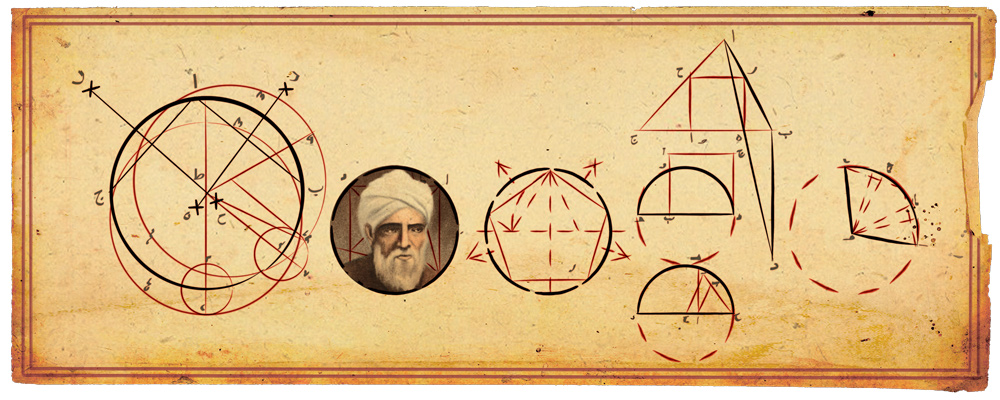

This beautiful doodle was published by google in the Persian and Arabic countries last 10th June because in 10th June 940 the great Abû al-Wafâ’ al-Buzjanî was born in Persia. Since 959, he worked in the Caliph’s court in Baghdad among other distinguished mathematicians and scientists who remained in the city after Sharâf al-Dawlâh became the new caliph in 983. He continued to support mathematics and astronomy and built a new observatory in the gardens of his palace in Baghdad (June 988) which included a quadrant over 6 metres long and a sextant of 18 metres.
Abû al-Wafâ’ wrote commentaries on works of Euclid, Ptolemy, Diophantus and al-Khwârizmî, and his works were very important in the developement of Trigonometry and Astronomy.